动态代理的使用。
概述
代理 (Proxy) 是一种设计模式,提供了对目标对象另外的访问方式;即通过代理对象访问目标对象.这样做的好处是:可以在目标对象实现的基础上,增强额外的功能操作,即扩展目标对象的功能。这里使用到编程中的一个思想:不要随意去修改别人已经写好的代码或者方法,如果需改修改,可以通过代理的方式来扩展该方法。
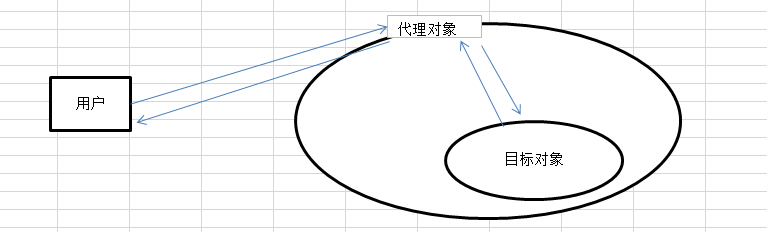
静态代理
这里使用明星与经纪人的关系来举个例子:很多明星出名之后,通告太多,邀请他的公司呢希望能一次性把费用和节目谈好,但是明星显然做不来这么多事情。于是经纪公司就对一人进行包装配备经纪人。从而形成一整套方案,这样满足甲方就非常方便了。
Java 中的静态代理类似于装饰者模式,静态代理在使用时,需要定义接口或者父类,被代理对象与代理对象一起实现相同的接口或者是继承相同父类。
1
2
3
| public interface People {
public void sing(String song);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @Slf4j
public class Star implements People {
@Override
public void sing(String song) {
log.debug("啊~" + song + "~~");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| @Slf4j
public class StarProxy implements People {
private People people;
public StarProxy(People people) {
this.people = people;
}
@Override
public void sing(String song) {
log.debug("接洽会谈");
people.sing("忘情水");
log.debug("收工打钱");
}
}
|
1
2
3
| People dehua = new Star();
StarProxy starProxy = new StarProxy(dehua);
starProxy.sing("忘情水");
|
动态代理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @Slf4j
public class StarFactory implements InvocationHandler{
private People people;
public StarFactory(People people) {
this.people = people;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
log.debug("商务洽谈");
Object o = method.invoke(people, args);
log.debug("收工打钱");
return o;
}
public Object getInstance() {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(people.getClass().getClassLoader(), people.getClass().getInterfaces(), this});
}
}
|
1
2
3
| People dehua = new Star();
People jjr = (People) new StarFactory(dehua).getInstance();
jjr.sing("忘情水");
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| @Slf4j
public class StarFactory {
private People people;
public StarFactory(People people) {
this.people = people;
}
public Object getInstance() {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(people.getClass().getClassLoader(), people.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
log.debug("商务洽谈");
Object object = method.invoke(people, args);
log.debug("收工打钱");
return object;
}
});
}
}
|
1
2
3
| People dehua = new Star();
People jjr = (People) new StarFactory(dehua).getInstance();
jjr.sing("忘情水");
|
CGLIB 动态代理
依赖
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>2.1_3</version>
</dependency>
|
代理类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @Slf4j
public class StarFactory2 implements MethodInterceptor {
public Object getInstance(Class clazz) {
Enhancer en = new Enhancer();
en.setSuperclass(clazz);
en.setCallback(this);
return en.create();
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
log.debug("商务洽谈");
Object returnValue = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
log.debug("收工打钱");
return returnValue;
}
}
|
1
2
3
| People dehua = new Star();
Star jjr = (Star) new StarFactory2().getInstance(Star.class);
jjr.sing("忘情水");
|
原理参考
https://www.jianshu.com/p/9a61af393e41
https://www.jianshu.com/p/471c80a7e831
Java 反射
反射 API 用来生成 JVM 中的类、接口或则对象的信息。
API
- Class 类:反射的核心类,可以获取类的属性,方法等信息。
- Field 类:Java.lang.reflec 包中的类,表示类的成员变量,可以用来获取和设置类之中的属性
值。
- Method 类: Java.lang.reflec 包中的类,表示类的方法,它可以用来获取类中的方法信息或
者执行方法。
- Constructor 类: Java.lang.reflec 包中的类,表示类的构造方法。
反射步骤
获取 Class 对象,调用对象方法。
- 获取想要操作的类的 Class 对象,他是反射的核心,通过 Class 对象可以任意调用类的方法。
- 调用 Class 类的方法,即反射的使用阶段
- 使用反射 API 来操作这些信息
获取 Class 对象的三种方法
-
调用某对象的 getClass() 方法
1
2
| Person p = new Person();
Class clazz = p.getClass();
|
-
调用某个类的 class 属性获取该类对应的 Class 对象
1
| Class clazz = Person.class;
|
-
使用 Class 类中的 forName() 静态方法,最安全,性能最好
1
| Class clazz = Class.forName("类的全路径");
|
获得了类对象之后,可以通过 Class 类中的方法获取并查看该类中的方法和属性:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| Class clazz = Class.forName("reflection.Person");
Method[] method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod();
for (Method m: method){
System.out.println(m.toString());
}
Field[] field = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f: field){
System.out.println(f.toString);
}
Constructor[] constructor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor c: constructor){
System.out.println(c.toString());
}
|
创建对象的两种方法
-
Class 对象的 newInstance()
使用 Class 对象的 newInstance()方法来创建该 Class 对象对应类的实例,但是这种方法要求该 Class 对象对应的类有默认的空构造器。
-
Constructor 对象的 newInstance()
先使用 Class 对象获取指定的 Constructor 对象,再调用 Constructor 对象的 newInstance()方法来创建 Clas 对象对应类的实例,通过这种方法可以选定构造方法创建实例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Class clazz = Class.forName("reflection.Person");
Person = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
Constructor c = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, String.class, int.class);
Person p1 = (Person) c.newInstance("张三", "男", 20);
|
